Definition:
In math, AND is a logical connector that means all connected conditions must be true at the same time. It’s most commonly used in logic, set theory, inequalities, probability, and computer science to show that multiple requirements apply together not separately.
At first glance, AND looks harmless. It’s one of the very first words we learn as kids. But in math, AND is powerful it can change answers, flip true to false, and decide whether a solution works or fails.
Students often get confused because AND in math doesn’t always behave like casual English. One missed detail treating AND like OR can cost full marks on a test or break a computer program.
This guide breaks it all down in plain, friendly language. By the end, you’ll understand exactly what AND means in math, how it’s used across topics, and how to avoid the most common mistakes.
What Does AND Mean in Math?
In math, AND means that every condition must be satisfied simultaneously.
If even one condition is false, the entire statement becomes false.
Quick way to remember:
- AND = all conditions must be true
- OR = at least one condition must be true
The Core Idea of AND in Mathematics
Think of AND as a gatekeeper 🚪
You only pass if you meet every requirement.
Real-life analogy:
To enter a movie rated PG-13, you must be 13 years old AND have a ticket.
If either condition fails, you don’t get in.
Math works the same way.
Origin of AND as a Mathematical Concept
The word AND comes from everyday English, but its formal mathematical meaning developed through:
- Ancient Greek logic (Aristotle’s syllogisms)
- Boolean algebra (George Boole, 1800s)
- Modern computer science and symbolic logic
In math, AND became a logical operator, often written symbolically as:
- ∧ (logical AND)
- ⋂ (intersection in sets)
How AND Is Used Across Different Math Topics
1. AND in Logic (Truth Statements)
In logic, AND connects two statements.
Statement form:
A AND B
This is true only if A is true AND B is true.
Truth Table for AND
| Statement A | Statement B | A AND B |
| True | True | ✅ True |
| True | False | ❌ False |
| False | True | ❌ False |
| False | False | ❌ False |
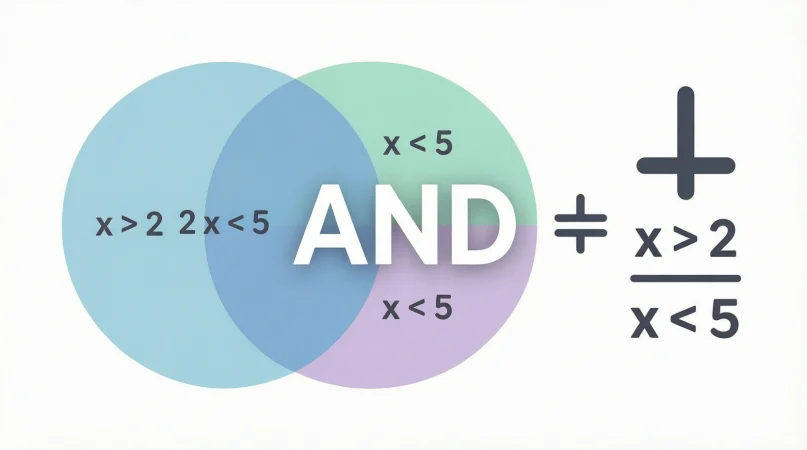
2. AND in Inequalities (Solving Math Problems)
AND is extremely common in inequalities.
Example:
x > 2 AND x < 5
This means:
- x must be greater than 2
- x must be less than 5
- Both conditions must hold
Solution:
2 < x < 5
3. AND in Set Theory (Intersections)
In sets, AND corresponds to intersection.
Example:
- Set A = even numbers
- Set B = numbers greater than 5
A AND B = numbers that are even AND greater than 5
Result: {6, 8, 10, …}
Symbol used:
- A ∩ B
4. AND in Probability
In probability, AND refers to joint events.
Example:
What is the probability of drawing a red card AND a face card?
You’re looking for outcomes that satisfy both conditions at once.
This is often written as:
- P(A AND B)
- P(A ∩ B)
5. AND in Algebra & Word Problems
Word problems frequently hide AND inside sentences.
Example:
A number is divisible by 2 AND 3.
This means:
- Divisible by 2
- Divisible by 3
→ So the number must be divisible by 6
6. AND in Computer Science & Programming
In coding, AND is a logical operator:
- Written as && (many languages)
- Written as AND (SQL, logic)
Example:
if (age > 18 && hasID)
The condition runs only if both are true.
AND vs OR in Math (Critical Comparison)
This is the most common confusion point.
Key Difference Table
| Feature | AND | OR |
| Meaning | All conditions must be true | At least one condition must be true |
| Strictness | Very strict | Flexible |
| Logical symbol | ∧ | ∨ |
| Set symbol | ∩ (intersection) | ∪ (union) |
| Common mistake | Treating AND like OR | Treating OR like AND |
Example:
- x > 2 AND x < 5 → Only numbers between 2 and 5
- x > 2 OR x < 5 → Almost all numbers
Tone & Meaning of AND in Math Statements
Unlike slang terms, AND in math has no emotional tone it’s neutral and precise.
However, misreading it can feel harsh 😅 because:
- One unmet condition = full rejection
- Partial correctness doesn’t count
That strictness is what makes math reliable.
Common Student Mistakes with AND
Avoid these traps:
- ❌ Solving only one condition
- ❌ Treating AND as OR
- ❌ Forgetting to combine solutions
- ❌ Ignoring boundary values
Pro tip:
Always ask:
Does my answer satisfy every part of the AND statement?
Alternate Meanings of AND (Outside Pure Math)
While AND in math is logical, it may appear differently elsewhere:
- English grammar: simple connector
- Computer hardware: AND gates
- Philosophy: conjunction
In math, though, the logical meaning always dominates.
Polite or Professional Alternatives
When teaching or writing formally, you might replace AND with:
- “Simultaneously”
- “At the same time”
- “Meeting both conditions”
- “Where both statements hold true”
These help clarify meaning without changing logic.
Labeled Example Table: AND in Action
| Math Statement | Meaning | Valid Solution |
| x > 1 AND x < 4 | Between 1 and 4 | x = 2 |
| Even AND divisible by 3 | Divisible by 6 | 12 |
| Red AND round | Both traits | Red ball |
| Pass math AND science | Both exams passed | Student qualifies |
Real-World Usage of AND in Math
AND shows up everywhere:
- 📊 Data filtering
- 🧮 Exams and homework
- 💻 Programming conditions
- 📈 Statistics and probability
- 🏗 Engineering logic
- 🧠 AI decision-making
If math models reality, AND defines the rules of reality.
FAQs
1. What does AND mean in math for kids?
It means everything listed must be true, not just one thing.
2. Is AND the same as plus?
No. AND is logical, plus is arithmetic. They do very different jobs.
3. How do I know if a problem uses AND?
Look for words like:
- and
- both
- simultaneously
- at the same time
4. What symbol represents AND in math?
- ∧ in logic
- ∩ in set theory
5. Can AND ever mean OR in math?
No. Never. They are strictly different.
6. Why is AND so strict?
Because math requires precision and certainty, not guesswork.
7. Is AND used in algebra?
Yes, especially in inequalities and word problems.
8. What’s the biggest mistake with AND?
Solving only one condition instead of all.
Conclusion
In math, AND is a small word with a big job. It tells us that all conditions must be true at the same time no shortcuts, no partial credit. Whether you’re working with logic statements, inequalities, sets, probability, or even computer code, AND acts as a strict connector that only allows results meeting every requirement.
The key to using AND correctly is slowing down and checking your answer against each condition, not just one. If even one part fails, the whole statement fails. Once you get comfortable spotting AND and understanding how it works, math problems become clearer, more logical, and much easier to solve with confidence.
Master AND, and you’ll avoid one of the most common math mistakes while building a strong foundation for higher-level math and real-world problem solving.

Michael Johnson is a seasoned Content Expert and digital communication specialist with a proven track record in content creation, strategy, and audience engagement. His work goes beyond writing he crafts meaningful, results driven content that helps businesses achieve growth, brand visibility, and audience trust.