Definition: eGFR (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate) is a blood test measurement that estimates how well your kidneys are filtering waste and excess fluid from your blood. It is calculated using your blood creatinine level along with factors such as age, sex, and sometimes race.
eGFR is one of those lab results that can look intimidating at first glance but once you understand it, it becomes a powerful tool for keeping tabs on your kidney health.
If you’ve ever looked at your blood test report and wondered “What does eGFR mean?” or “Is my eGFR number good or bad?”, you’re not alone. This guide breaks it all down in plain, human language no medical degree required.
In short:
👉 eGFR tells doctors how well your kidneys are working.
Why eGFR Matters (Quick Overview)
Your kidneys filter about 120–150 quarts of blood every day, removing toxins and balancing fluids. When kidney function declines, waste builds up and that’s where eGFR becomes crucial.
Doctors use eGFR to:
- Detect early kidney disease
- Monitor chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Adjust medication dosages safely
- Track kidney health over time
What Does eGFR Stand For? (Origin and Meaning)
Let’s break down the abbreviation:
- e = estimated
- GFR = Glomerular Filtration Rate
What is a glomerulus?
A glomerulus is a tiny filter inside your kidney. Each kidney has about one million of them. Together, they filter waste, salt, and excess water from your blood.
Because directly measuring GFR is complex and invasive, doctors use eGFR, a calculated estimate based on bloodwork.
How Is eGFR Calculated?
eGFR is calculated using:
- Serum creatinine (from a blood test)
- Age
- Sex
- Body size
- Sometimes ethnicity (older formulas included race; newer ones often do not)
Common eGFR formulas:
- CKD-EPI (most widely used today)
- MDRD (older method)
💡 Important note: eGFR is an estimate, not a direct measurement but it’s accurate enough for clinical use in most people.
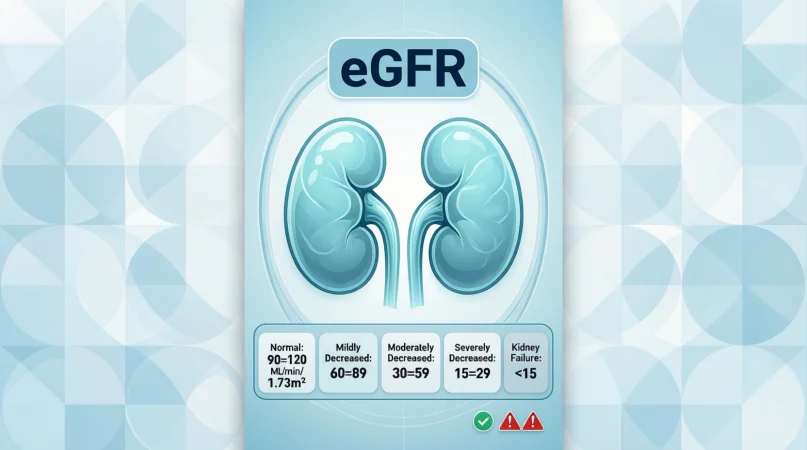
Normal eGFR Ranges Explained
Here’s what those numbers usually mean 👇
eGFR Reference Table
| eGFR Value (mL/min/1.73m²) | Kidney Function Level | Meaning |
| 90 or higher | Normal | Healthy kidney function |
| 60–89 | Mildly reduced | Often normal with aging |
| 45–59 | Mild to moderate decrease | Early CKD (Stage 3a) |
| 30–44 | Moderate to severe decrease | CKD Stage 3b |
| 15–29 | Severe decrease | CKD Stage 4 |
| Below 15 | Kidney failure | CKD Stage 5 |
⚠️ Doctors usually don’t diagnose kidney disease unless eGFR stays below 60 for 3 months or more.
What Is a “Good” eGFR by Age?
eGFR naturally declines as you get older. That doesn’t always mean disease.
Average eGFR by Age
| Age Range | Average eGFR |
| 20–29 | ~116 |
| 30–39 | ~107 |
| 40–49 | ~99 |
| 50–59 | ~93 |
| 60–69 | ~85 |
| 70+ | ~75 |
📌 A slightly lower eGFR in older adults can be normal aging, not kidney failure.
What Causes a Low eGFR?
A low eGFR means your kidneys aren’t filtering as efficiently. Common causes include:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Dehydration
- Heart disease
- Kidney infections
- Certain medications (NSAIDs, some antibiotics)
Temporary drops can also happen due to:
- Illness
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Low fluid intake
Can eGFR Improve Over Time?
Yes sometimes! 🎉
eGFR can improve if the cause is temporary or treatable, such as:
- Dehydration
- Medication side effects
- Acute kidney injury (AKI)
However, in chronic kidney disease, eGFR usually declines gradually, though lifestyle changes can slow progression.
eGFR vs Creatinine: What’s the Difference?
These two often appear together on lab reports.
Comparison Table
| Test | What It Measures | What It Tells You |
| Creatinine | Waste product in blood | How much waste kidneys fail to remove |
| eGFR | Estimated filtration rate | Overall kidney function |
🧠 Key takeaway:
Creatinine is the raw number; eGFR turns it into a meaningful kidney health score.
eGFR vs BUN vs Creatinine Clearance
Here’s how they differ:
- eGFR: Best overall snapshot of kidney function
- BUN: Affected by diet and hydration
- Creatinine clearance: More precise but requires 24-hour urine collection
Doctors prefer eGFR for routine monitoring because it’s:
- Fast
- Reliable
- Easy to track over time
Examples of eGFR in Context
✅ Friendly/Neutral Medical Context
- “Your eGFR is 92, which means your kidneys are working well.”
⚠️ Concerned but Professional
- “Your eGFR has dropped to 55, so we’ll monitor for early kidney disease.”
❌ Dismissive or Misleading (Not Recommended)
- “Your eGFR is low, but it’s probably nothing.”
(Doctors should always investigate persistent low values.)
Real-World Usage: When Doctors Use eGFR
eGFR is commonly used to:
- Diagnose chronic kidney disease
- Monitor kidney health in diabetes
- Adjust chemotherapy or antibiotic doses
- Decide if imaging contrast dye is safe
- Evaluate transplant eligibility
It’s one of the most important routine blood test values in modern medicine.
Alternate Meanings of eGFR
In medical contexts, eGFR almost always refers to kidney function.
In rare research settings:
- It may appear in renal physiology studies
- Outside medicine, it has no common alternate meaning
So if you see eGFR on a blood test yes, it’s about your kidneys.
Professional and Patient-Friendly Language Tips
Instead of saying:
- “Your kidneys are failing”
Doctors often say:
- “Your kidney function is reduced”
- “Your eGFR is lower than expected”
This keeps communication accurate, calm, and respectful.
FAQs:
1. What does eGFR mean on a blood test report?
It shows how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood.
2. What is a dangerous eGFR level?
An eGFR below 30 is considered severe and requires close medical care.
3. Is eGFR the same as kidney function?
Yes eGFR is the standard estimate doctors use to assess kidney function.
4. Can dehydration lower eGFR?
Yes. Dehydration can temporarily raise creatinine and lower eGFR.
5. What eGFR indicates kidney failure?
An eGFR below 15 usually indicates kidney failure (Stage 5 CKD).
6. Can diet affect eGFR results?
Indirectly. High protein intake, supplements, or poor hydration can affect creatinine levels.
7. Should I worry if my eGFR is 60?
Not always. Doctors usually look for persistent levels below 60 over several months.
8. How often should eGFR be checked?
- Healthy adults: during routine bloodwork
- CKD patients: every 3–6 months (or as advised)
Conclusion
So, what does eGFR mean in a blood test? Simply put, it’s your kidneys’ report card. It helps doctors spot problems early, adjust treatments safely, and protect one of the most essential systems in your body.
Understanding your eGFR empowers you to ask better questions, make informed health choices, and stay proactive about kidney health long before serious problems arise.

Megan Lewis is a passionate and experienced content writer specializing in creating engaging and well-researched content. She excels at producing clear, informative, and reader-focused content that not only ranks well on search engines but also delivers real value to audiences.